What is IPoDWDM?
IP over DWDM eases IP optical networks
The evolution of coherent transport technology and photonic integration has made it possible to develop coherent pluggable transceivers in small form factors, such as QSFP28 and QSFP-DD. These next-generation transceivers can be plugged directly into routers, enabling IP-over-DWDM (IPoDWDM) architectures that integrate IP and optical layers, require less equipment and help minimize cost, power consumption and footprint. By reducing the need for intermediate transponders and simplifying the number of elements that need to be installed, managed and maintained, IPoDWDM offers a more streamlined approach to IP-centric networks. However, this architectural shift also introduces challenges – particularly around management, pluggable transceiver visibility and ensuring router compatibility with new pluggables.
Built on open, disaggregated infrastructure
IPoDWDM architectures rely on an open line system (OLS), enabling operators to mix and match routers, pluggables and OLS from multiple vendors.
IPoDWDM architectures require less equipment, helping minimize cost, power and space.
Multi-vendor interoperability
The Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF) leads standardization for coherent transceivers and CMIS management, boosting vendor compatibility for IPoDWDM networks.

Avoid vendor lock-in through open standards
Industry bodies like the OIF, OpenROADM and OpenZR+ have defined interoperability specifications that enable multi-vendor coherent pluggable transceivers of an IPoDWDM system to work together. What’s more, the OIF’s Common Management Interface Specification (CMIS) supports consistent management of pluggable modules across host platforms such as routers, while open network management interfaces such as OpenConfig and T-API support multi-vendor orchestration, enabling seamless automation and end-to-end service visibility across both IP and optical layers. With operators able to leverage best-of-breed solutions from different vendors, they can build more capable, efficient and economical networks.
IPoDWDM deployment scenarios
IPoDWDM is gaining traction across AI-driven data center interconnect (DCI) environments, with adoption expanding from hyperscalers to service providers and enterprises alike.
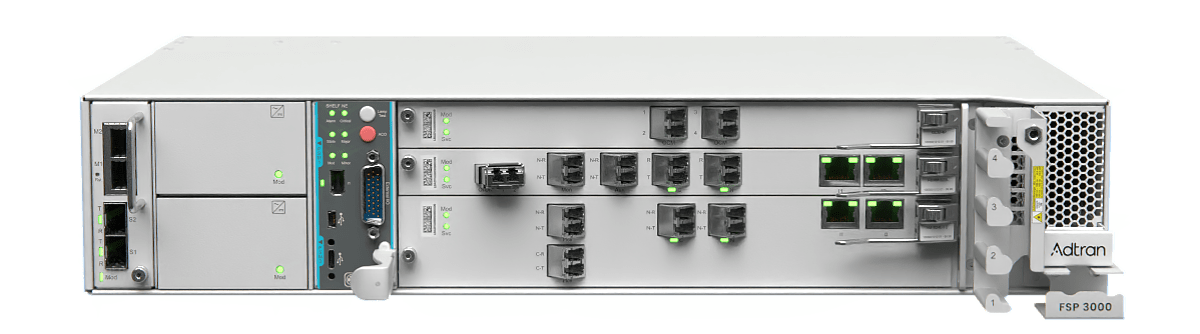
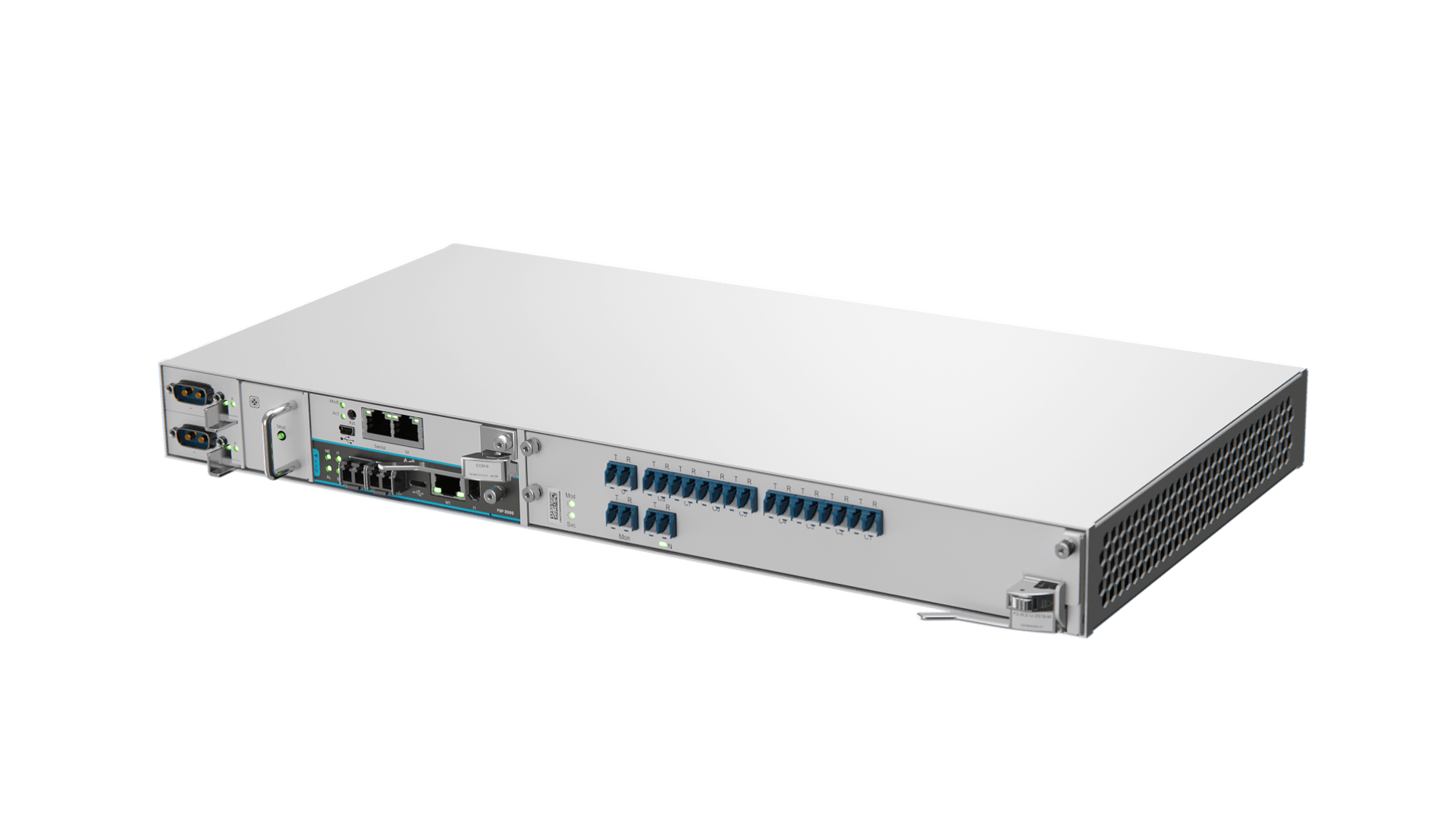
Scalable bandwidth for IP-centric optical networks
IPoDWDM can be implemented using a variety of optical network architectures. One of the most common deployment models uses short-reach point-to-point links (typically up to 120km) and ZR/ZR+ coherent optics. For this use case, our FSP 3000 IP OLS is specifically engineered to deliver maximum simplicity and performance. With a compact and user-friendly design, it enables the transport of both Adtran and third-party ZR/ZR+ coherent pluggable transceivers from 100Gbit/s to 1.6Tbit/s. This high-density solution integrates an 8-channel mux/demux filter (expandable to 16), two EDFA with automated power control, optical channel monitoring and OTDR-based fiber monitoring into a single card that can be housed in a 1RU chassis, fitting any installation environment. With zero-touch provisioning, automated processes and built-in monitoring functions, operators and enterprises have a simple, plug-and-play route to leveraging IPoDWDM and scaling bandwidth, even without optical expertise.
Related resources
 ;
;


